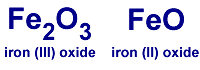What will happen to the world if there are no more metals?
A metals is a chemical element that is a good conduct of both electricity and heat and forms cations and ionic bonds with non-metals
Each metal has its especial uses and it will depend largely on what you are going to make as to the kind of metal you should make it of.
Metals are present in minute quantities in all living organisms. Na and K are major metals that that are used for transmission of electrical signals from the brain to the entire nervous system. Iron is an important component of hemoglobin in the blood of warm-blooded animals. Iron transports oxygen to issues by forming oxides. In cold-blooded animals, blood contains copper. Chlorophyll in plants contains magnesium. Other metals like copper, zinc etc. are needed by different tissues in a human body for functioning properly. So that if no more metals in the earth, living organisms will not be as right now, even do not exist.
Metals play a different part of living life. For example, the use of aluminium is drinks can, cooking pots, overhead power cables. We use copper for water pipes, electrical wires; iron for bridge construction, building construction… If in the earth there are no more metals all thing are made of it would not exist. So that the earth could not be develop like right now
What is the reason to recycling metals:
It is easy and cost-effective to recycle metal, and metal can be recycled continuously without losing its properties. In addition, recycling metal reduces the environmental impacts associated with metal mining and production. According to Waste Online:
Recycling aluminium requires only 5% of the energy and produces only 5% of the CO2 emissions as compared with primary production and reduces the waste going to landfill. Aluminium can be recycled indefinitely, as reprocessing does not damage its structure. Aluminium is also the most cost-effective material to recycle.
Recycling one tonne of steel cans saves 1.5 tonnes of iron ore, 0.5 tonnes of coal & 40% water usage.
Recycling 1 tonne of steel scrap saves 80% of the CO2 emissions produced when making steel from iron ore.
Isn’t it easier to obtain metals through it s original form through extraction of metals?
It is very hard to extraction metals. There are a number of different methods of metal extraction, including:
• by heating with carbon (in the form of coke)
• by heating with a more reactive metal (active metal)
• by electrolysis of melts
• by reduction with hydrogen gas
• Which method is used depends on:
1) the energy requirements extraction uses large amounts of energy (electricity and / or heat)
2) the cost of the reductant carbon (in the form of coke), which is cheap, is widely used, but sometimes more reactive metals are required which are very costly
3) the metal purity required the higher the required purity, the greater the cost in obtaining that purity
The effect to environment in the recycling of metals:
a) Recycling metals
• We need to recycle metals as supplied will not last forever (for some metals this would happen in our lifetimes).
• Recycling metals:
• saves resources (e.g. metal ores)
• creates less waste (e.g. mining waste)
• saves energy resources (less energy to re-cycle than make from ore, e.g. recycling Al uses 5% of energy used to extract)
• reduces air pollution (e.g. CO2 – greenhouse effect, SO2 – acid rain, CO - toxic)
• However, there are costs associated with sorting and transporting metals to be recycled that have to be factored into the overall financial and energy costs.
b) Recycling copper
• One way to recycle copper is to react scrap copper with sulphuric acid or a specific enzyme to form solutions containing Cu2+(aq).
• The copper can be extracted by reaction with scrap iron: Cu2+(aq) + Fe(s) → Cu(s) + Fe2+(aq)
• This method can also be used to extract copper from low grade ores.
Think of reactive ways, that we can also play a part in recycling metals:
- We can stop use drink cans install of that we use polycarbonate bottle.
- We reuse wires
- We made windows and door frames as wood
- Collect the metals for recycling
Recycled metals products:
Source:
http://www.zerowastesg.com/2008/12/08/metal-recycling/
http://www.educationalelectronicsusa.com/c/metals-XV.htm
Wednesday, 21 September 2011
Wednesday, 6 July 2011
chemical formula
Jöns Jacob Berzelius [jœns ˌjɑːkɔb bæɹˈseːliɵs] (20 August 1779 – 7 August 1848) was a Swedis chemist. He worked out the modern technique of chemical formula notation, and together with John Dalton, Antoine Lavoisier, and Rbert Boyle considered of modern of chemistry.
Jons Jacob Berzelius ‘’invented’’ a system of chemical notation in 1811. The system is based on the ‘’law of definite proportions’’, stating that all samples of a given chemical compound have the same elemental composition.
What are chemical formulas?
-Chemical formulas are short-hand representations of compounds using chemical symbols and oxidation numbers. (Oxidation is defined as the interaction between oxygen molecules and all the different substances they may contact, from metal to living tissue)
How to write chemical formulae?
+Binary compound:
-The simplest chemical formulas are for binary compounds: make up of 2 elements. they have a positive half and a negative half. The positive half is written first, the negative second. - The key point to write chemical formulas is the oxidation number /valency/ the charge. We can see it in the Periodic Table directly. With the transition metals and any atoms that act in unusual ways, will be provided. The metals have a positive oxidation number, the non-metals have a negative oxidation number. Special with element hydro, it is non-metal but it has positive charge 1+.
-
- - The sum of the oxidation numbers in a compound must equal zero
- -The oxidation number of an ion is equal to its charge
-
MExample:
- Subscripts: small numbers to the lower right of a symbol. They represent the number of atoms of that element in the compound
In iron (III) oxide: it has 2 iron atoms, 3 oxygen atoms in the compound.
In iron (II) oxide: it has 1 iron atom, 1 oxygen atom in the compound.
Subscript of 1 are “understood”, never written.
Polyatomic ions ( ions made up of more than one atom)
- Write their formulas just like binary compounds
- List of polyatomic ions:
- The polyatomic ion may be either the positive or the negative half of the formula – or both
- If more than one polyatomic ion is needed in a formula, put parentheses around the ion add the subscript outside the parenthesis. This is the only time parenthesis are used in a chemical formula
Magnesium hydroxide
Calcium sulphate
Does the ate present 3 oxygen?
- There are a lot of ions with the –ate: acetate ion, nitrate ion, chlorate ion, sulphate ion, carbonate ion, phosphate ion…
- The ate does not present 3 oxygen. For example: sulphate ion SO4 2-, phosphate ion PO4 3-
- The –ate have 1 more oxygen than the -ites and their charge does not change as the result. For example: nitrate NO3 – then nitrite is NO2 -; phosphate is PO4 3- then phosphate is PO3 3-
- The –ate with charges less than negative 1 ( that is , ions with charge of -2, -3, etc.) can have an H added to them to form new polyatomic ions. For each H added, the charge is increased by a+1. For example: CO3 2- then added H and become HCO3 -
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)